
When the R allele (red petal) recombines with the r allele (white petal trait), neither allele is fully dominant so neither is able to express its trait fully. This Punnett square illustrates incomplete dominance. If one parent is BB and one is Bb, there is a 50% chance of having a BB child and a 50% chance of having a Bb child, but all children this couple produces will have brown eyes. If one of the parents is BB, it is impossible for the child to have blue eyes, as the table below shows. The last scenario (bb) shows how it is possible for the offspring to inherit recessive alleles from both parents, and thereby display a recessive phenotype even though neither of its parents does. 3 of the 4 scenarios modeled in the Punnett square show at least one B allele. In such a scenario where both parents carry a dominant and recessive allele, there is a 75% chance the child will have brown eyes (BB or Bb) and a 25% chance he or she will have blue eyes (bb). Notice from the table above that both parents have brown eyes, but they also both have recessive alleles that they might pass on to a child. If both parents contribute the recessive allele (b), the child will be bb and have blue eyes, even though both parents may have brown eyes themselves. This is because the dominant allele (B) will override the recessive one (b).

The child will also have brown eyes if she inherits the dominant allele (B) from one parent and the recessive allele (b) from the other parent. If both parents contribute the dominant (B) allele, the child will be BB and have brown eyes. The allele for brown eyes is upper case B and for blue eyes is lower case b. Immediately below is a Punnett square, a table that demonstrates the probability of inheriting a certain trait, which in this case is eye color. Note that genetic inheritance is complex and cannot always be explained in this simple manner - some people have green eyes, for example, and or one blue eye and one brown eye ( heterochromia iridum). The genotype is considered heterozygous when an individual has one dominant allele and one recessive allele. The genotype is considered homozygous when an individual has either two dominant alleles or two recessive alleles. This genetic material, which determines traits (the phenotype) is called the genotype. Thus, in the case of Bb (dominant and recessive), brown (B) dominates and determines the eye color. But if she receives recessive alleles from both parents (bb), she will have blue eyes.
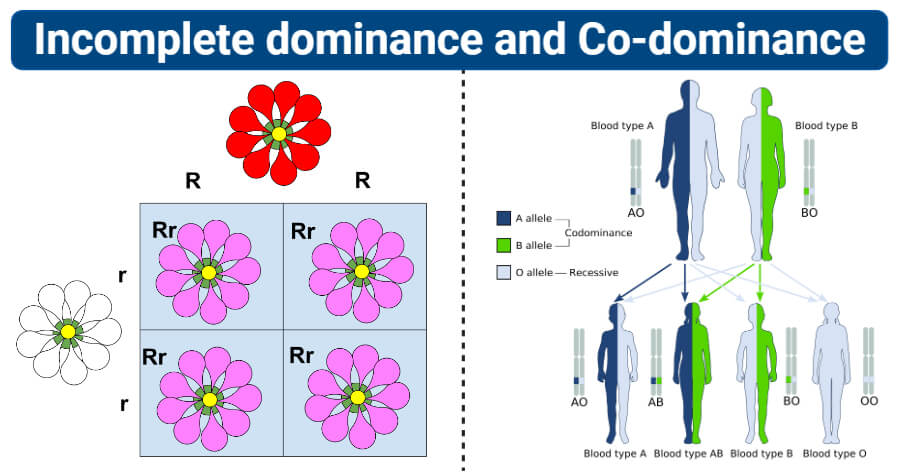
If she receives a dominant allele from one parent and a recessive gene from the other (Bb) she will also have brown eyes. If a person receives dominant alleles from both parents (BB) she will have brown eyes. With respect to eye color, the allele for brown eyes (B) is dominant, and the allele for blue eyes (b) is recessive.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
